Conventionally, in Geopolymer bricks (GPBs), fly ash from power plants and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) are converted into bricks by chemical treatment. In this work, a novel GPB has been obtained by adding nano silica and rice husk ash along with conventional ingredients of GPB. In solar drying, paraffin wax is employed for accelerating the curing time by utilizing its latent heat stored in the form of phase change. It has been experimentally found that solar drying method with paraffin wax utilizes shorter curing time when compared to electrical oven curing and open sun drying. The properties of novel GPB are evaluated by mechanical testing and compared with conventional GPB. It has been experimentally observed that novel GPB exhibits higher mechanical properties when compared to conventional GPB. Also in this study, SEM images (2\(\mu\)m, 5 KX), (3\(\mu\)m, 4 KX), (10\(\mu\)m, 1 KX), (20\(\mu\)m, 500X), (100\(\mu\)m, 250X) and EDX analysis of novel GPB obtained from test results have been furnished. Smart quantitative results from EDX analysis show that O K has the highest weight percentage and atomic percentage.
Energy from the sun is a potential candidate, compared to other sources in several areas like agriculture, distillation, construction and other industries [1]. Green house en- ergy is an open method when compared to other modes of drying [2]. Open sun drying and its risk factors pose a threat to the drying process [3]. The risk factors of green house energy method can be eliminated by convection based solar dryers which is also safe for the environment [4]. A solar dryer was proposed as a substitute for electric dryer; to prove its efficiency [5]. Phase change materials are materials to regulate a bandwidth of temper- atures, by utilizing its latent heat, in several applications like buildings to minimize con- sumption of energy [6]. Phase change material like paraffin suffers negligible volume changes during phase change process making it easier to incorporate it in equipments [7]. Paraffin wax can maintain a hotter environment than the ambience at least for a span of five hours after the sunset, thereby reducing the curing time [8]. Composite phase change material is used as coatings on building wall to regulate indoor temperature [9]. Paraffin wax absorbed into fly ash ceramsite is used as PCM to tackle massive energy consumption [10]. In construction industries GPBs are a potential threat to sand and cement bricks with good structural properties even at elevated temperatures [11]. Also in comparison with other conventional bricks, GPBs are affordable while economy and eco-friendliness is con- cerned [12]. Author investigated strength, microstructure and curing time of GPBs [13]. Authors suggested efficient drying range of temperatures between 40°C to 60 °C for evolving GPBs in construction industries. [14]. Polymer composites are finding applications even in construction areas, like use of poly- mer in bricks [15, 16]. Construction industries need bricks of less energy consumption and pollution which inculcates hybrid solar dryer in building applications [17]. Rice husk ash is finding applications in manufacturing of sustainable GPBs [18]. Nano clay and granite dust are alternative replacement for cement mortars to bring down carbon dioxide emis- sions [19]. Use of GPBs in terms of strength compared to the conventional bricks comes under the modified guidelines of GPBs concrete mix design using Indian standards [20].
This work deals with the preparation of a novel GPB, comparison of drying methods like electrical drying, solar drying with a PCM (Paraffin Wax) and solar drying without a PCM, in terms of curing time and mechanical property comparison of novel GPB with conventional GPB.
At Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Tamil Nadu (India), a solar dryer of dimensions (710 * 310 * 310) with all dimensions in millimeters was fabricated as shown in Figure 1. The dryer set up contains iron stand drying chamber and UV-coated parabolic polycarbonate sheets for absorbing incident solar energy. An aluminum frame is used to structurally support the polycarbonate sheet. A Cudappah stone of dimension (695 mm * 295 mm) is kept below polycarbonate sheet to constrain transfer of heat in downward direction for obtaining uniform drying temperature. The dryer shows four ny- lon wheels at the bottom to move the dryer for convenience. Solar powered photovoltaic (PV) panel fan is provided to remove saturated air and allow fresh atmospheric air into the chamber. On the basis of curing temperature, this fan automatically turns on and off during the process. Latent heat storage material like paraffin wax is kept in a steel con- tainer above the Cudappah stone has 57.5 °C as melting point temperature. Material prop- erties of paraffin wax are predicted in Table 1.
| PCM |
Melting
Temperature (°C) |
Density (kg/m3) | Specific Heat (J/Kgk) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
Latent Heat of
Fusion (kJ/kg) |
|||
| Solid | Liquid | Solid | Liquid | Solid | Liquid | |||
| Paraffin wax | 57.5 | 915 | 815 | 2005 | 2095 | 0.225 | 0.245 | 205 |

| Material | Weight in kg/m3 |
|---|---|
| Fly ash | 286 |
| GGBS | 166 |
| M sand | 580 |
| Coarse aggregate 20 mm | 865 |
| AAS—alkaline activated solution | 336 |
| SSS—sodium silicate solution Na2SiO3 | 240 |
| NaOH | 96 |
| NaOH molarity | 12 |
| Alkaline/binder ratio | 0.61 |
| Rice husk ash | 82.5 |
| Nano silica | 16.5 |
| Precursor | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | Na2O | SO3 |
| Fly Ash | 52 | 27 | 3.5 | 9.25 | 7.5 | 1.55 | 0.845 | 0.725 | 0.545 |
|
Ground granulated
blast furnace slag |
35 | 14 | 36 | 7.5 | 0.545 | 0.45 | 0.725 | 0.25 | 1.65 |
| Nano silica | 90.5 | 0.082 | 0.059 | 0.081 | 0.011 | 0.02 | – | 0.89 | 0.23 |
| Rice husk ash | 85.85 | 0.19 | 1.95 | 0.375 | 1.98 | 0.09 | – | 0.39 | – |
| Test | Geometry | Length | Breadth | Height | Diameter | STANDARD |
| Tensile split strength | Cylindrical | 20 | 10 | ASTM C496-96 | ||
| Compressive strength | Cubic | 10 | 10 | 10 | ASTM E9-19 | |
| Flexural strength | Rectangular | 50 | 10 | 10 | ASTM D790-17 |








The specification of electric oven used for curing is shown below:
-Power rating = 3600 Watts,
-Voltage rating = 225 V,
-Frequency = 50 Hz.
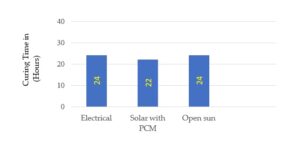
At the beginning of curing process, the GPB exhibits fluctuations in weight. As it gets stabilized, the moisture content had been completely cured. The time consumed for dry- ing moisture content is 24 hours. Further the GPBs were allowed to develop proper strength at room temperature for 28 days. This same procedure was applied for all curing methods mentioned below.
The drying process took 22 hours.
The drying process took 24 hours.
Results of mean value of two specimens in each test have been established in Figures 10-13 with the following inference: The temperature in electric oven drying was around 65°C while temperature in solar drying operates at around 60°C, with variations depending on atmospheric conditions. As per the observations from Figure 10, it is un- derstood that solar drying with a PCM consumes almost two hours less curing time among all curing methods for novel GPB.
According to Indian standards, compressive strength for conventional GPB is around 30 MPa [20]. In this work, the compressive strength from experiment, predicts a value of 45 MPa for novel GPB in solar drying with a PCM, as shown in Figure 11. Also for novel GPB, tensile split strength of 4.5 MPa and flexural strength of 6.5 MPa was obtained in solar drying with a PCM, as shown in Figure 12 and 13 respectively.
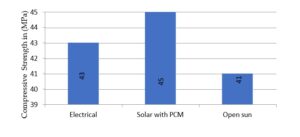

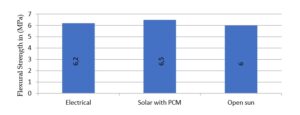
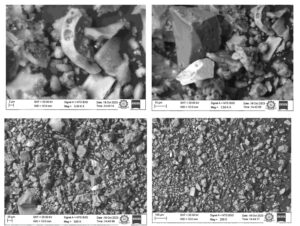
Experimentally, it is evident from Figure 11-13 that novel GPB under solar drying with a PCM exhibit 4.65% and 9.76% higher compressive strength, 5.88% and 12.5% higher tensile split strength, and 4.84% and 8.33% higher flexural strength when compared to electrical drying and open sun drying respectively. Specimen under solar dryer with PCM has been selected for SEM and EDX analysis. Specimen and surface topo- graphical images of tensile split strength test, compression test and flexural test captured by SEM have been shown below in Figures 14 and 17, 19, 21 respectively to have an idea of microstructure. An EDX analysis of specimen under tensile split strength, com- pression test and flexural test have been shown in Figure 18, 20, and 22 which predicts O K as the highest by weight and atomic percentage in all the three test.






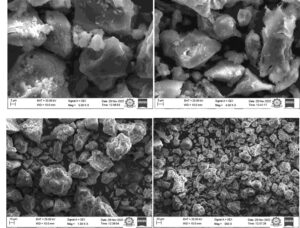
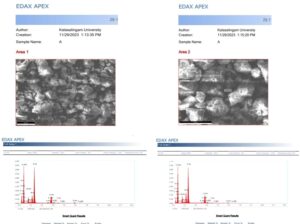
It is evident from Table 4, that novel GPB under solar drying is the most efficient with 22 hours of curing time due to latent heat storage [5, 21]. It is evident from Tables 5-8 that novel GPB exhibits higher tensile split strength, higher compressive strength and higher Flexural Strength when compared to conventional GPB for all the curing methods [21]. This is due to the presence of Nano silica and Rice Husk Ash in the novel GPB which gives better bonding effect when compared to conventional GPB. Also for novel GPB, so- lar drying with a PCM shows higher compressive strength, tensile split strength, and flex- ural strength when compared to electrical drying and open sun drying due to higher la- tent heat storage [21].
| Conventional GPB | Novel GPB | |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Curing Time (Hours) | Curing Time (Hours) |
| Electrical drying | 24 | 24 |
| Solar drying (PCM) | 22 | 22 |
| Open-sun drying | 24 | 24 |
| Conventional GPB | Novel GPB | Percentage Difference | |
| Drying Method | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |
| Electrical drying | 38.5 | 43 | 11.68 |
| Solar drying (PCM) | 41.5 | 45 | 8.43 |
| Open-sun drying | 37 | 41 | 10.81 |
| Conventional GPB | Novel GPB | Percentage difference | |
| Drying Method | Tensile Split Strength (MPa) | Tensile Split Strength (MPa) | |
| Electrical drying | 3.10 | 4.25 | 37.09 |
| Solar drying (PCM) | 3.35 | 4.5 | 34.32 |
| Open-sun drying | 2.9 | 4 | 37.93 |
| Conventional GPB | Novel GPB | Percentage difference | |
| Drying Method | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | |
| Electrical drying | 4.95 | 6.2 | 25.25 |
| Solar drying (PCM) | 6.20 | 6.5 | 4.83 |
| Open-sun drying | 6.70 | 6 | 10.5 |
For novel GPB, solar dryer with a PCM consumes 22 hours of curing time which is less than all other methods [5, 21].
As per Indian standards, compressive strength for conventional GPB is 30 MPa [20, 22]. In this work for novel GPB under a solar-dried with PCM, the experiment value shows 45 MPa which is favourable for construction industries.
The presence of nano silica and rice husk ash proves that novel GPB exhibits higher compressive strength, tensile split strength, and flexural strength when compared to conventional GPB [21, 23], for all curing methods respectively, except for open sun drying method under flexural strength test , which may be due to increase in brittleness due to the addition of nano silica.
Novel GPB, under solar drying with a PCM shows higher compressive strength, ten- sile split strength, and flexural strength when compared to electrical drying and open sun drying which promotes the use of PCMs in curing of bricks and enhancing the strength of bricks in construction industries on large scale basis [21].
Due to the important contribution of silica in construction industries, silica has been used as a target to predict its contribution in GPBs.
Conceptualization, Ashok Kumar J. and Muthuvel S.; meth- odology, Ashok Kumar J and Muthuvel S.; software, R.S.P.; validation, Ashok Kumar J. and Muthuvel S.; formal analysis,.; investigation, Ashok Kumar J.; resources, Ashok Kumar J.; data curation, Ashok Kumar J.; writing—original draft preparation, Muthu- vel S.; writing—review and editing, R.S.P., Velmurugan and Gianpaolo Di Bona; visu- alization,.; supervision, Muthuvel S.; project administration, .; funding acquisition,. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Azaizia, Z., Kooli, S., Hamdi, I., Elkhal, W., & Guizani, A. A. (2020). Experimental study of a new mixed mode solar greenhouse drying system with and without thermal energy storage for pepper. Renewable Energy, 145, 1972-1984.
Gorjian, S., Hosseingholilou, B., Jathar, L. D., Samadi, H., Samanta, S., Sagade, A. A., … & Sathyamurthy, R. (2021). Recent advancements in technical design and thermal performance enhancement of solar greenhouse dryers. Sustainability, 13(13), 7025.
Sridhar, K., & Charles, A. L. (2022). Mathematical modeling to describe drying behavior of kyoho (Vitis labruscana) skin waste: drying kinetics and quality attributes. Processes, 10(10), 2092.
Elavarasan, E., Kumar, Y., Mouresh, R., & Natarajan, S. K. (2022). Experimental investigation of drying tomato in a double slope solar dryer under natural convection. In Advances in Mechanical and Materials Technology: Select Proceedings of EMSME 2020 (pp. 179-190). Springer Singapore.
Capossio, J. P., Fabani, M. P., Reyes-Urrutia, A., Torres-Sciancalepore, R., Deng, Y., Baeyens, J., … & Mazza, G. (2022). Sustainable solar drying of brewer’s spent grains: a comparison with conventional electric convective drying. Processes, 10(2), 339.
Saliby, A., & Kovács, B. (2023). Minimization of annual energy consumption by incorporating phase change materials into building components: A comprehensive review. Heat Transfer Research, 54(13), 65-91.
Saikia, D., Nayak, P. K., Krishnan, K. R., Kondareddy, R., & Lakshmi, D. V. N. (2022). Development of indirect type solar dryer and experiments for estimation of drying parameters of dhekia (Diplazium esculentum). Materials Today: Proceedings, 56, 774-780.
Badaoui, O., Hanini, S., Djebli, A., Haddad, B., & Benhamou, A. (2019). Experimental and modelling study of tomato pomace waste drying in a new solar greenhouse: Evaluation of new drying models. Renewable Energy, 133, 144-155.
Geng, Z., Shi, C., Zhao, Q., & Yang, L. (2024). Preparation of diatomite paraffin composite phase change coating and its simulation application in building wall. Journal of Energy Storage, 83, 110543.
Wang, X., Li, W., Huang, Y., Zhang, S., & Wang, K. (2023). Study on shape-stabilised paraffin-ceramsite composites with stable strength as phase change material (PCM) for energy storage. Construction and Building Materials, 388, 131678.
Albitar, M., Visintin, P., Mohamed Ali, M. S., & Drechsler, M. (2015). Assessing behaviour of fresh and hardened geopolymer concrete mixed with class-F fly ash. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 19, 1445-1455.
Bai, Y., Guo, W., Wang, J., Xu, Z., Wang, S., Zhao, Q., & Zhou, J. (2022). Geopolymer bricks prepared by MSWI fly ash and other solid wastes: Moulding pressure and curing method optimisation. Chemosphere, 307, 135987.
Shi, H., Ma, H., Tian, L., Yang, J., & Yuan, J. (2020). Effect of microwave curing on metakaolin-quartz-based geopolymer bricks. Construction and Building Materials, 258, 120354.
Maaze, M. R., & Shrivastava, S. (2023). Design development of sustainable brick-waste geopolymer brick using full factorial design methodology. Construction and Building Materials, 370, 130655.
Ganesh, A. C., & Muthukannan, M. (2021). Development of high performance sustainable optimized fiber reinforced geopolymer concrete and prediction of compressive strength. Journal of Cleaner Production, 282, 124543.
Shanmugam, V., Rajendran, D. J. J., Babu, K., Rajendran, S., Veerasimman, A., Marimuthu, U., … & Ramakrishna, S. (2021). The mechanical testing and performance analysis of polymer-fibre composites prepared through the additive manufacturing. Polymer Testing, 93, 106925.
Partheeban, P., Jegadeesan, V., Manimuthu, S., & Gifta, C. C. (2024). Cleaner production of geopolymer bricks using Solar-LPG hybrid dryer. Journal of Cleaner Production, 442, 141048.
Bahrami, A. (2024). Sustainable Structures and Buildings (p. 122). Springer Nature.
Owaid, H. M., Humad, A. M., Al-Gburi, M., Ghali, Z. A. S., & Sas, G. (2023). Utilization of nanoparticles and waste materials in cement mortars. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Materials, 32(1), 20220289.
Anuradha, R., Sreevidya, V., Venkatasubramani, R., & Rangan, B. V. (2012). Modified guidelines for geopolymer concrete mix design using Indian standard. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 13, 353–364.
Ashok Kumar, J., Muthuvel, S., Issac Selvaraj, R. V., Ramoni, M., Shanmugam, R., & Pandian, R. S. (2023). Mechanical Property Comparison of Geopolymer Brick Dried by Electrical and Passive Solar Devices with Phase Change Material (Paraffin Wax). Processes, 12(1), 28.
Standard, I. (2009). Guidelines for concrete mix design proportioning. Bureau of Indian Standard, New Delhi.
Ashok Kumar, J., Muthuvel, S., Issac Selvaraj, R. V., Ramoni, M., Shanmugam, R., & Pandian, R. S. (2024). Mechanical Property Comparison of Geopolymer Brick Dried by Electrical and Passive Solar Devices with Phase Change Material (Paraffin Wax). Processes, 12(1), 28.